3.37 Brain Anatomy
Our brain helps us do everything it enables us to breathe, keeps our heart beating, helps us ride a bicycle, allows us to see color, and so much more. Learn about the different parts of your brain and the jobs they perform.
Parts of the Brain
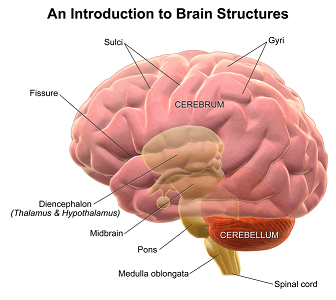
Your brain weighs about two to three pounds, and it may be the most important two to three pounds of your body! The brain controls every action and activity. It’s responsible for our breathing, our heartbeat, and even our thoughts and feelings. People have been fascinated by the brain for centuries, but scientists are just beginning to unravel its mysteries. The brain is made up of three major parts: they’re called the brain stem, the cerebellum, and the cerebrum.
The brain stem connects the base of the brain to the spinal cord. It’s the part of the picture that looks like a stem. The brain stem is important in keeping you alive. It controls critical functions like your heart rate, breathing, and sleep and wake cycles.
The brain stem connects to the cerebellum. This part of the brain is responsible for muscle control, balance, and coordination. It helps you with everything from playing sports to writing your homework.
Diagram showing some of the main areas of the brain

The largest part is called the cerebrum. The cerebrum is divided into different parts called lobes. Each lobe has its own job to do, but all of the lobes work together to help us respond to the world around us.
1. Main points:
The brain, weighing two to three pounds, controls vital functions and activities, comprising the brain stem (controlling critical functions), cerebellum (responsible for muscle control and coordination), and cerebrum (divided into lobes for various tasks).
2. Questions:
- Content Analysis: What are the three major parts of the brain and their primary functions?
- Contextual Analysis: How does the structure of the brain contribute to its various functions?
- Linguistic Analysis: What words in the text highlight the importance and complexity of the brain?
3. Further Discussion:
Why do you think the brain needs different parts to control different functions?
4. Answers:
- Content Analysis: "The brain stem… controls critical functions like your heart rate, breathing, and sleep and wake cycles. The cerebellum… is responsible for muscle control, balance, and coordination. The cerebrum… is divided into different parts called lobes."
- Contextual Analysis: The text describes how "The brain stem connects to the cerebellum," and "The largest part is called the cerebrum," indicating the interconnected structure contributing to various functions.
- Linguistic Analysis: Words like "controls," "responsible," and "critical functions" highlight the brain’s importance and complexity.
The Lobes
If you look down on a human brain from overhead, you will notice that it appears to be divided in half. These sides are the left and right hemispheres of the cerebrum. They are connected in the middle.
The left and right sides of the cerebrum are joined in the middle
Each lobe has a right side and a left side. The very front of the brain is made up of the frontal lobe. This lobe helps you plan your day, stay organized in school, and keep your feelings under control.
The parietal lobe sits just behind the frontal lobe, stretching from the middle to the back of the skull. It allows you to notice touch, heat, cold, and pain. If you touch a hot stove, it’s your parietal lobe that lets you know.
The cerebrum is made up of parts called lobes

The temporal lobe sits just behind and above the ears. It serves an important role in hearing and memory. If you’ve had the same song stuck in your head all day, thank your temporal lobe!
Finally, the occipital lobe is in the back of the skull, just above the neck. It makes sense out of the things we see, like shapes and colors. Look around the room for a minute; what do you see? A desk, a rug, or a chair perhaps? You can thank your occipital lobe for identifying those things for you.
You just learned that the brain is made up of different parts, but what makes up those parts? The brain is made of billions of tiny nerve cells called neurons. You need a powerful microscope to see neurons, and you need all sorts of fancy equipment to see the work they do.
1. Main points:
The cerebrum is divided into left and right hemispheres, with lobes responsible for planning and emotions (frontal lobe), sensation (parietal lobe), hearing and memory (temporal lobe), and vision (occipital lobe), all made up of billions of neurons.
2. Questions:
- Content Analysis: What are the functions of the four lobes of the cerebrum?
- Contextual Analysis: How does the division of the cerebrum into hemispheres and lobes contribute to its functionality?
- Linguistic Analysis: What words in the text help us understand the specific functions of each lobe?
3. Further Discussion:
Why do you think the brain needs different lobes for different senses and functions?
4. Answers:
- Content Analysis: "Frontal lobe helps you plan your day… Parietal lobe allows you to notice touch, heat, cold, and pain… Temporal lobe serves an important role in hearing and memory… Occipital lobe makes sense out of the things we see."
- Contextual Analysis: The text describes the specific functions of each lobe, showing how the division into different areas allows for specialized functions.
- Linguistic Analysis: Words like "plan," "notice," "hearing," "memory," and "makes sense out of" help us understand the specific functions of each lobe.
Lesson Summary
The brain has three major parts. The brain stem looks like a stem. It keeps us alive by helping us breathe and controlling our heartbeat and sleep and wake cycles. The cerebellum, connected to the brain stem, helps us with physical activities like muscle control, balance, and coordination. It helps us write and ride a bike.
The cerebrum is divided into lobes: the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes, and performs many important functions. The frontal lobe helps us plan and organize. The parietal lobe allows us to feel things like heat, cold, pain, and pressure. The temporal lobe is the center of hearing and memory. The occipital lobe makes sense out of the things our eyes see. Finally, nerve cells, called neurons, are the building blocks of the brain.
Additional Activities
Brain Anatomy: Crossword Puzzle
In this activity, you’ll check your knowledge regarding the functions and parts of the brain.
Directions
Complete the crossword by filling in a word that fits each of the given clues. For this activity, you’ll need a printer to reproduce the following page. With a pencil and an eraser, neatly write your answers in the boxes provided.

Across
-
The occipital lobe is the part of the human brain responsible for interpreting information from the __________.
-
__________ and muscle coordination are managed by the cerebellum.
-
The forebrain, or the __________, is the largest and most developed part of the brain.
-
At the area behind the forehead lies the __________ lobe that controls emotions.
-
The parietal lobe processes information relating to __________, taste, and temperature.
Down
-
Our cerebrum is divided into the left and right hemispheres that are joined in the __________.
-
__________ are specialized cells in the brain designed to transmit information to other cells.
-
Each of the components of the brain __________ functions to help regulate breathing and heartbeat.
-
The __________ is an organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information, and manages emotions.
-
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the brain that sits close to the __________.
Answer Key

